1 南京大学固体微结构物理国家重点实验室,江苏 南京 210093
2 南京大学现代工程与应用科学学院,江苏 南京 210023
3 南京大学物理学院,江苏 南京 210093
4 南京大学人工微结构科学与技术协同创新中心,江苏 南京 210093
5 南京信息工程大学大气物理学院,江苏 南京 210044
为了实现远程气体探测,基于由超晶格材料构成的光参量振荡器,研制了一台双波长输出的中红外激光器。该光参量振荡器通过种子注入的方式,实现了纳秒级窄线宽的中红外脉冲激光输出,重复频率为500 Hz,单脉冲能量超过1 mJ,并能够对准2.6~4.0 μm波长范围内的NO、NO2和SO2的吸收峰。通过气体动态排放实验,在远程气体探测实验中对该激光器进行了验证。
光参量 窄线宽 光谱 中红外激光器 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(1): 0114001
1 山东大学新一代半导体材料研究院晶体材料国家重点实验室, 山东 济南 250100
2 南京大学固体微结构物理国家重点实验室, 江苏 南京 210093
基于光学超晶格的光参量振荡技术是研制2~5 μm波段中红外相干光源的有效技术手段,在遥感探测、精密测量、环境监测、医疗诊断、科学研究和****等领域具有非常重要的应用价值。总结了光学超晶格2~5 μm中红外光参量振荡器的国内外研究进展,重点分析了连续波、纳秒脉冲以及皮秒脉冲等不同运转模式下光参量振荡器的结构特点、优势和发展前景。并对光学超晶格中红外光参量振荡器的发展趋势进行了展望,指出高功率、宽调谐、低功耗、小型化和轻量化是光学超晶格光参量振荡器的重要发展方向,而高质量大尺寸(厚度)的光学超晶格晶体、性能优异的泵浦源和可靠的工程化样机设计是未来光参量振荡器发展的核心技术。
激光光学 光学超晶格晶体 光参量振荡器 中红外激光
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, School of Physics, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, and Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Institute for Quantum Information and State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, College of Computing, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 Mesoscopic Optics and Quantum Electronics Laboratory, University of California Los Angeles, California, CA 90095, USA
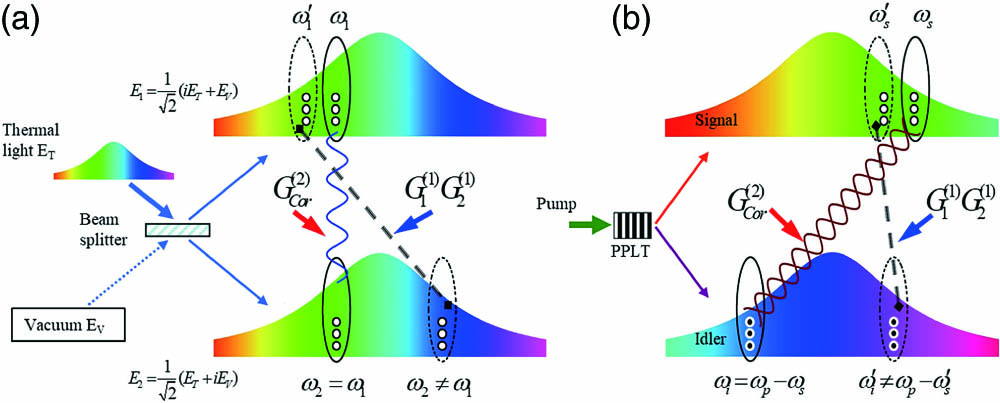
We report an observation of the second-order correlation between twin beams generated by amplified spontaneous parametric down-conversion operating above threshold with kilowatt-level peak power, from a periodically poled LiTaO3 crystal via a single-pass scheme. Photocurrent correlation was measured because of the bright photon streams, with raw visibility of 37.9% or 97.3% after electronic filtering. As expected in our theory, this correlation is robust and insensitive to parametric gain and detection loss, enabling important applications in optical communications, precision measurement, and nonlocal imaging.
amplified spontaneous parametric down-conversion robust second-order correlation high-gain twin beams Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(12): 121902

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
Alloying in two-dimension has been a hot spot in the development of new, versatile systems of optics and electronics. Alloys have been demonstrated to be a fascinating strategy to modulate the chemical and electronic properties of two-dimensional nanosheets. We firstly reported ultra-broadband enhanced nonlinear saturable absorption of Mo0.53W0.47Te2 alloy at 0.6, 1.0, and 2.0 μm. The nonlinear saturable absorption of Mo0.53W0.47Te2 saturable absorber (SA) was measured by the open aperture Z-scan technique. Compared to MoTe2 and WTe2 SAs, the Mo0.53W0.47Te2 SA showed five times deeper modulation depth, 8.6% lower saturable intensity, and one order larger figure of merit. Thus, our research provides a method of alloys to find novel materials with more outstanding properties for optics and optoelectronic applications.
nonlinear optics transition metal dichalcogenides saturable absorption Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(2): 021902
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
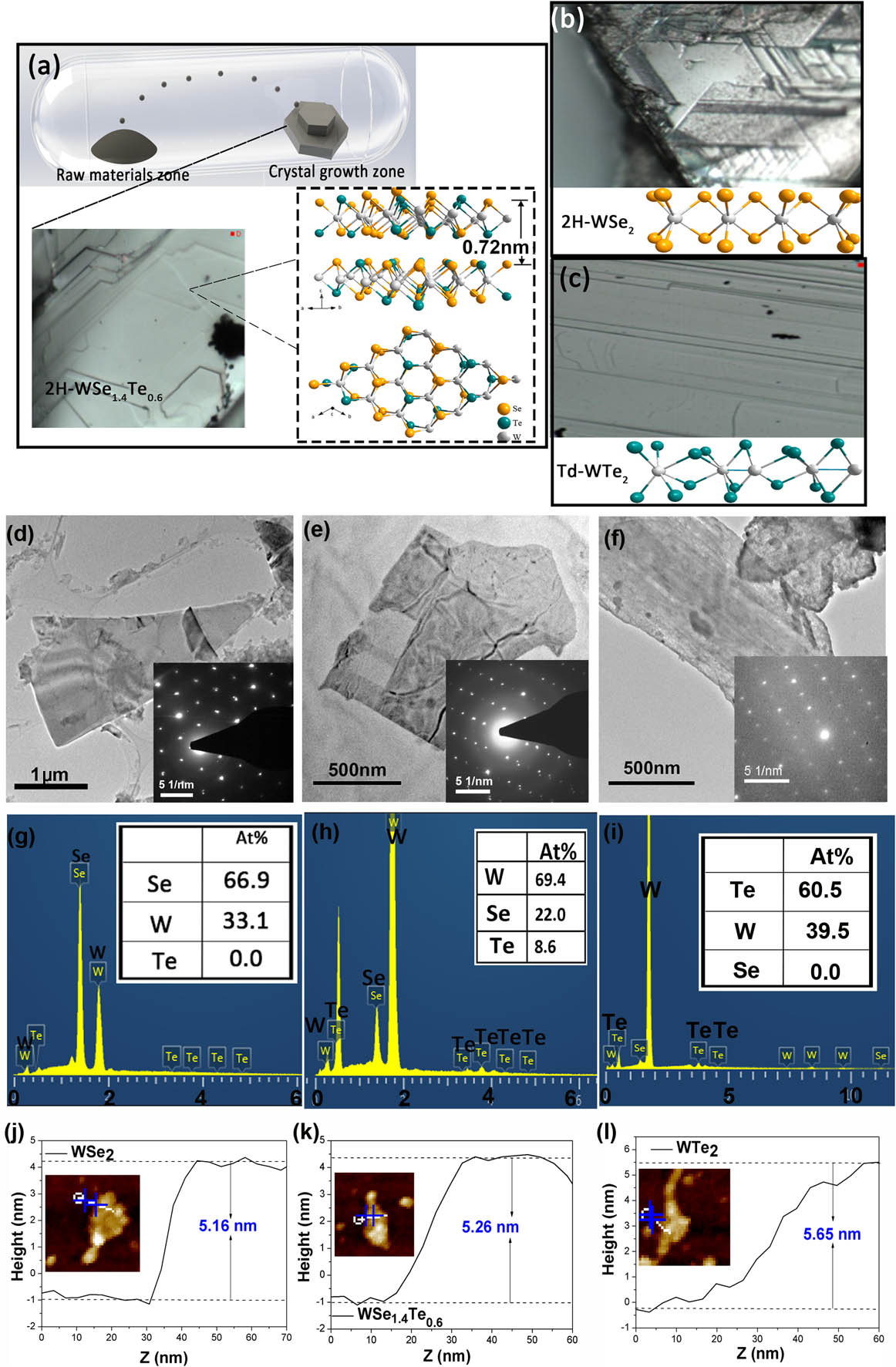
Due to the composition-dependent properties of two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), alloying of existing dissimilar TMDs architecture is a novel and controllable route to tailor crystal structures with superior optical and optoelectronic properties. Here, we reported the hexagonal-phase WSe1.4Te0.6 alloy can enable great promise for enhanced saturable absorption response exceeding the parent component WSe2 and WTe2, with larger modulation depth and lower saturable intensity. These advantages allowed the 1064 nm passively Q-switched lasers based on WSe1.4Te0.6 to be more efficient, with pulse duration narrowed to 45%, and slope efficiency increased by 232%. Our findings highlighted the appropriate alloying of TMDs as an effective strategy for development of saturable absorbers.
140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 160.4236 Nanomaterials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(12): 121404
1 南京大学固体微结构物理国家重点实验室, 江苏 南京 210093
2 南京大学现代工程与应用科学学院, 江苏 南京 210093
利用分步傅里叶算法结合坐标变换理论,建立了在光致折射率改变介质中任意形状光束的传输、聚焦模拟方法,能够用于计算任意光束形状、任意介质厚度的Z扫描开孔和闭孔拟合曲线。在薄介质和高斯光束条件下,该方法的拟合曲线与经典算法相吻合。在平顶光束情况下,该方法的拟合结果与实验数据基本一致。利用此方法测量了LiTaO3晶体的非线性吸收和非线性折射率系数,并对高斯光束和涡旋光束在厚介质中的Z扫描过程进行了分析。
激光光学 Z扫描 傅里叶变换 厚介质 光学学报
2014, 34(12): 1214002
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所上海市全固态激光器与应用技术重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 100049
3 南京大学物理学院, 江苏 南京 210093
通过准相位匹配技术,采用1 μm波段高功率窄谱线连续光纤激光放大器抽运高二次谐波转换效率周期性极化晶体,是实现高光束质量、小型化、高功率连续绿光激光器的一个非常有前途的方向。实验自主研发了高效率主振荡功率放大(MOPA)全光纤保偏放大模块,获得中心波长为1064.25 nm,线宽为0.035 nm的30 W连续线偏振激光,并以此作为基频光抽运国产周期极化钽酸锂(PPSLT)晶体进行了外腔单通倍频实验。保持PPSLT晶体的控制温度为145.6 ℃,在抽运光功率为21.5 W时得到了2.1 W的绿光输出。实验分析了温度、基频光功率密度和Boyd-Kleinman聚焦因子对倍频光转换效率的影响。实验过程中没有出现饱和现象,进一步提高抽运功率有望获得更高功率的绿光。
激光器 主振荡功率放大 双包层光纤激光 倍频 周期极化钽酸锂晶体





